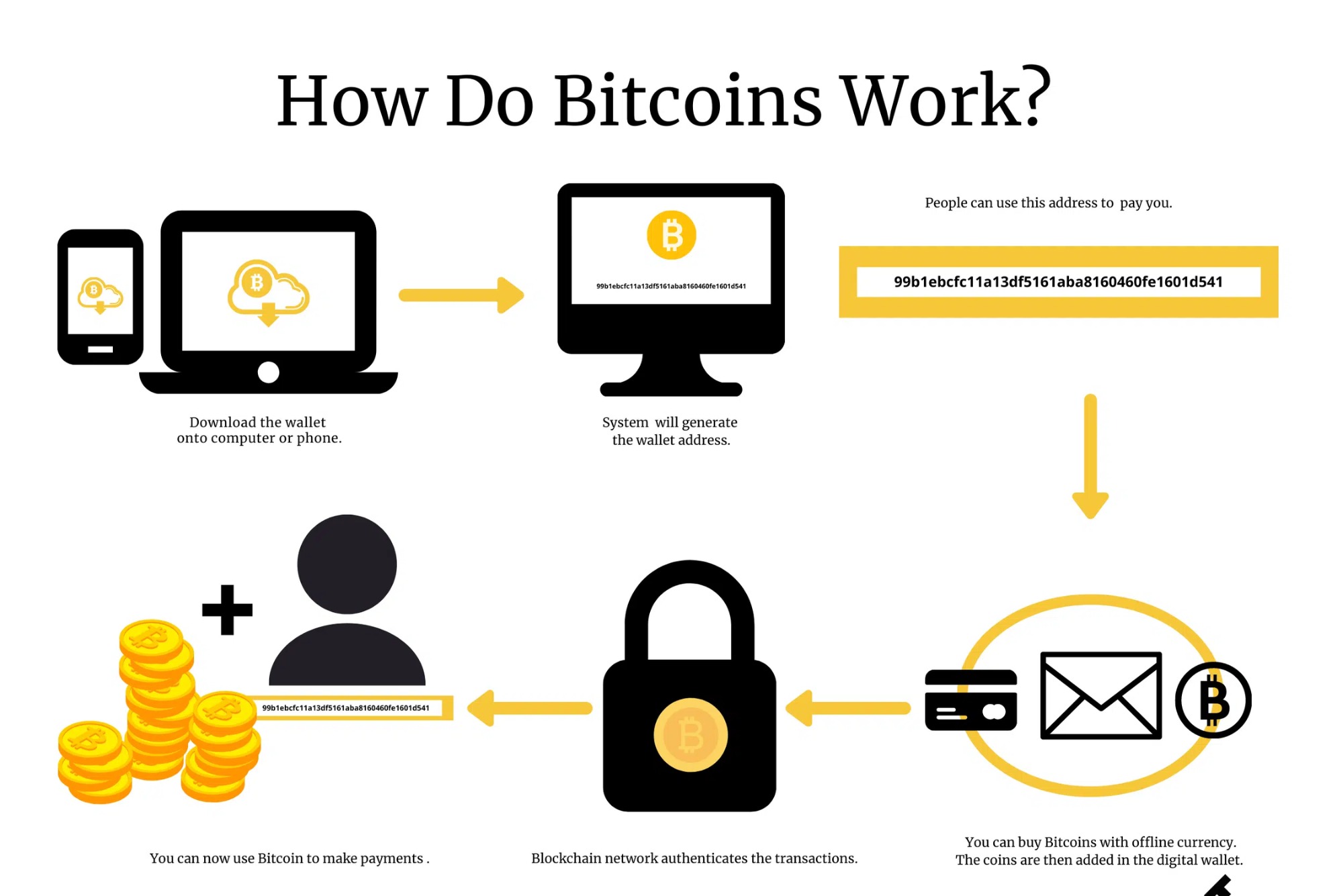
In the realm of finance and technology, Bitcoin has emerged as a revolutionary form of currency. But what exactly is Bitcoin, and how does it function within the global economy? Let’s delve into the fundamental nature of Bitcoin as a currency.
Bitcoin: A Digital Currency
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, often referred to as a cryptocurrency. Unlike traditional fiat currencies issued by governments and regulated by central banks, Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network, allowing for direct transactions without intermediaries.
Characteristics of Bitcoin
Decentralization
Decentralization refers to the distribution of authority, control, and decision-making away from a central authority or governing body. This concept is particularly significant in the context of various systems, including political, economic, and technological frameworks. In political terms, decentralization can manifest as the delegation of powers from a central government to regional or local governments, thereby allowing for greater autonomy and responsiveness to local needs.
This can enhance democratic engagement by enabling citizens to have a more direct influence over local governance, fostering accountability and transparency. Economically, decentralization can facilitate competition among businesses, leading to innovation and more efficient resource allocation. In this context, decentralized markets can provide more opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises, as they are less hindered by regulatory burdens imposed by a centralized authority.
In the realm of technology, decentralization has gained prominence through the advent of blockchain and distributed ledger technologies. Unlike traditional systems where a single entity holds power over data and processes, decentralized systems distribute this power among numerous participants, enhancing security and reducing the risk of fraud. For example, in cryptocurrency networks like Bitcoin, transactions are verified by a network of nodes rather than a central authority.
This not only increases the resilience of the system but also empowers individuals by giving them greater control over their assets and data. Decentralization in this sense promotes transparency, as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that can be audited by anyone, reducing the potential for manipulation.
Moreover, decentralization can lead to enhanced innovation. By reducing the barriers to entry in various industries, decentralized systems can create a more level playing field where individuals and smaller entities can participate and compete. This democratization of access can stimulate creativity and the development of new ideas, as diverse voices contribute to the evolution of products and services.
However, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges associated with decentralization. While distributing power can lead to more responsive governance and innovation, it can also result in fragmentation and inefficiencies. For example, in a decentralized political system, coordination between different levels of government can be complex, potentially leading to conflicting policies and regulatory uncertainty. Similarly, in decentralized technological systems, issues such as scalability, governance, and security need to be carefully managed to prevent exploitation and ensure functionality.
In conclusion, decentralization is a multifaceted concept that holds significant implications across various domains. By dispersing power and control, it can enhance democratic engagement, foster innovation, and increase security, particularly in technological contexts. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of decentralization largely depends on how well the challenges it presents are addressed. As society continues to evolve in the face of rapid technological advancements and changing political landscapes, the ongoing discourse around decentralization will remain vital in shaping a more equitable and innovative future.
One of the defining features of Bitcoin is its decentralized nature. Transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of nodes. This decentralization ensures transparency and security, as no single entity controls the Bitcoin network.

Limited Supply
Unlike fiat currencies that can be printed indefinitely, Bitcoin has a finite supply. The total number of Bitcoins that can ever exist is capped at 21 million, making it a deflationary asset. This scarcity is one of the factors driving the value of Bitcoin.
Digital Nature
Bitcoin exists solely in digital form, stored in digital wallets and transferred electronically. What Type of Currency Is Bitcoin This digital nature allows for borderless transactions and facilitates accessibility for users around the world.
Uses of Bitcoin
Store of Value
Many investors view Bitcoin as a digital gold, a store of value that can hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty. Its limited supply and decentralized nature make it an attractive asset for long-term investment.
Medium of Exchange
While Bitcoin’s primary use case has evolved from a means of exchange to a store of value, it is still used for everyday transactions by a growing number of merchants and individuals. However, scalability issues and price volatility have hindered its widespread adoption as a medium of exchange.
Investment Vehicle
Bitcoin has gained popularity as an investment vehicle, with many investors buying and holding it for potential price appreciation. Its volatile nature presents both opportunities and risks for traders seeking to profit from price fluctuations.
Implications of Bitcoin
Disruption of Traditional Finance
The rise of Bitcoin poses a challenge to the traditional financial system, offering an alternative to centralized banking and government-controlled currencies. Its decentralized nature empowers individuals to have greater control over their finances and transactions.

Regulatory Challenges
As Bitcoin continues to gain mainstream acceptance, regulators around the world are grappling with how to classify and regulate it. The lack of a central authority overseeing Bitcoin raises concerns about money laundering, tax evasion, and consumer protection.
Technological Innovation
Beyond its role as a currency, Bitcoin has spurred innovation in blockchain technology, the underlying technology that powers it. Blockchain has applications beyond finance, including supply chain management, identity verification, and voting systems.
Bitcoin represents a paradigm shift in the world of finance, challenging traditional notions of currency and value. Its decentralized nature, limited supply, and digital properties make it a unique asset with profound implications for the future of money and technology.
Bitcoin Price Now
As of [current date], the price of Bitcoin stands at [current price]. Bitcoin’s price Now is subject to volatility due to various factors, including market demand, regulatory developments, and macroeconomic trends. Investors should exercise caution and conduct thorough research before engaging in Bitcoin transactions.