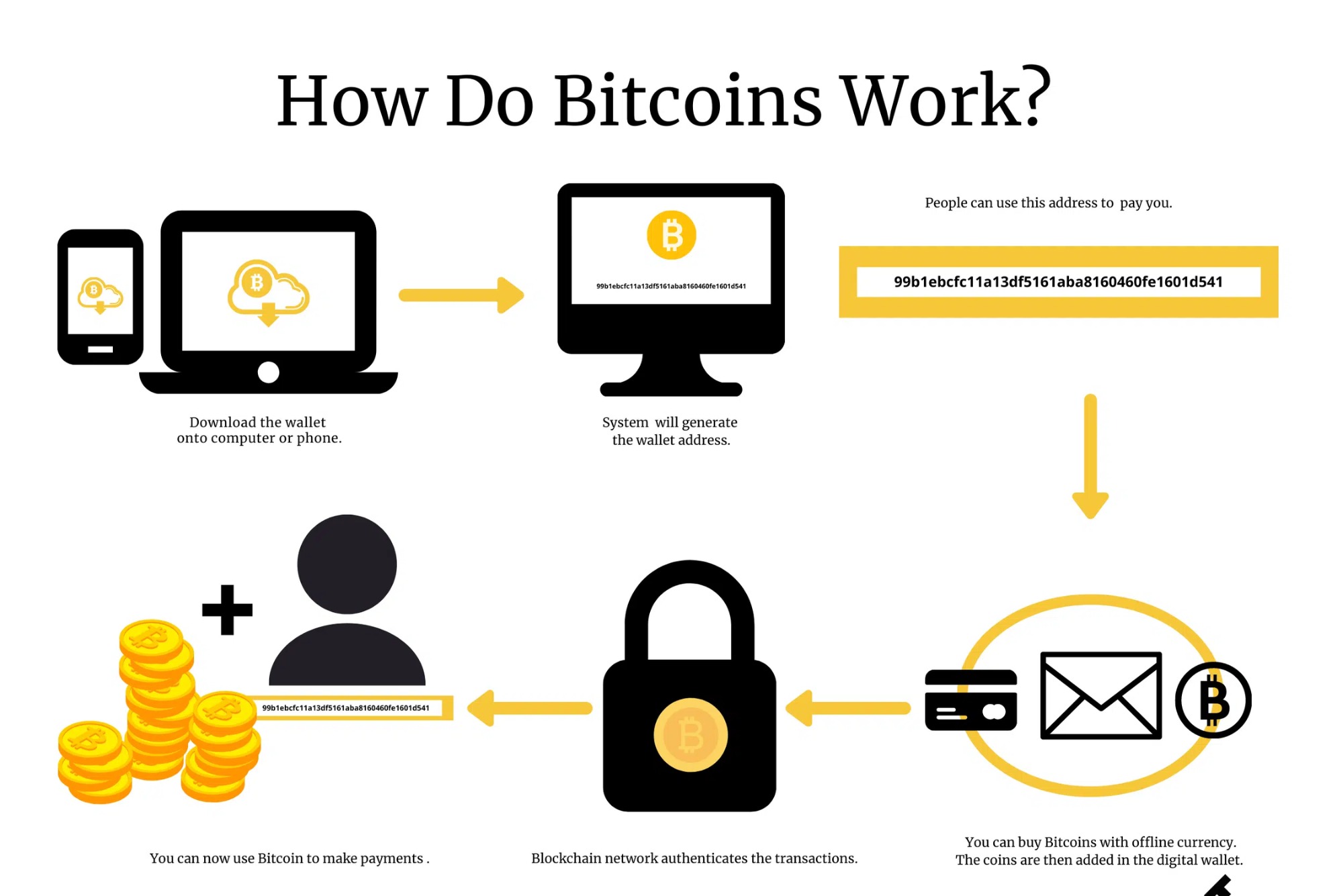
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has captivated the world with its decentralized nature and potential for financial revolution. Understanding how Bitcoin operates is essential for anyone looking to delve into the realm of digital currency.
The Blockchain Technology
At the heart of Bitcoin lies blockchain technology. Blockchain serves as a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Each block contains a set of transactions, cryptographically linked to the preceding block, forming an immutable chain.
Cryptography: Securing Transactions
Cryptography plays a pivotal role in securing Bitcoin transactions. Public and private keys enable users to send and receive Bitcoin securely. Transactions are verified through cryptographic algorithms, ensuring authenticity and integrity.

Mining: Securing the Network
Mining is the process by which new bitcoins are created and transactions are validated. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, adding new blocks to the blockchain and securing the network. In return, miners are rewarded with bitcoins.
Decentralization: Eliminating Intermediaries
One of Bitcoin’s most groundbreaking features is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin operates without a central authority, such as a government or financial institution. How Does Bitcoin Work This decentralization promotes transparency, security, and financial sovereignty.
Peer-to-Peer Transactions
Bitcoin enables peer-to-peer transactions, allowing users to send and receive funds directly without intermediaries. This peer-to-peer network facilitates fast, efficient, and borderless transactions, empowering individuals worldwide.
Wallets: Storing Bitcoin Securely
Wallets serve as digital containers for storing bitcoins. They come in various forms, including software, hardware, and paper wallets. Each wallet generates unique addresses for sending and receiving Bitcoin, providing users with full control over their funds.
Transaction Verification: Confirming Legitimacy
Every Bitcoin transaction undergoes verification by nodes on the network. Nodes validate transactions based on consensus rules, ensuring their legitimacy. Once verified, transactions are added to the blockchain and become irreversible.
Scalability Challenges
Despite its revolutionary potential, Bitcoin faces scalability challenges. The limited block size and increasing transaction volume have led to congestion and high fees. Efforts are underway to address these issues through solutions like the Lightning Network and Segregated Witness (SegWit).

Future Outlook
As Bitcoin continues to evolve, its future remains a subject of speculation and debate. From mainstream adoption to regulatory scrutiny, Bitcoin’s journey is marked by both opportunities and challenges. Nevertheless, its underlying principles of decentralization and financial sovereignty continue to resonate with individuals worldwide.
Bitcoin Legend Listing Date
The “Bitcoin legend listing date” refers to the historic moment when Bitcoin was first listed on a cryptocurrency exchange. On July 18, 2010, the now-defunct exchange Mt. Gox listed Bitcoin for the first time, marking a significant milestone in the cryptocurrency’s journey. This event not only provided a platform for trading Bitcoin but also contributed to its growing recognition and adoption within the digital currency community. Today, the listing date holds historical significance as it symbolizes Bitcoin’s emergence as a viable alternative to traditional currencies.